Advanced R
Data visualization with ggplot2
Alice Zhao
Fall 2025
Introduction to ggplot
Part of the tidyverse, ggplot2 is an R
package that implements the “grammar of graphics” in R.
In ggplot, graphics are built by supplying data and mapping of data values to aesthetics, and then adding layers that build geometric objects, scales, labels, and more.
Why ggplot?
- Highly customizable and extensible.
- Designed to work with
dplyrand othertidyversepackages. - In use for over 10 years, meaning that help is widely available.
- Wide variety of avilable extensions
Useful resources
- The ggplot cheatsheet
- The ggplot reference guide
- The Data Visualization chapter in the “R for Data Science” book
- And, of course, the help files that come with the package itself.
Let’s make sure we have the necessary data frames for our examples
- If you still have
imports,generation,merged_energy,long_genandlong_merged_energyin your Enrivorment, read ingapminderand recreategapminder07. - Alternatively, or if you are missing any of those objects from your workspace, run the following line of code:
Basics: grammar of graphics
Components of a basic plot
- data: a data frame, provided to
the
ggplot()function - geometric objects: the
objects/shapes that you want to plot, indicated through one of the many
available
geomfunctions, such asgeom_point()orgeom_hist() - aesthetic mapping: the mapping
from the data to the geometric objects, provided in an
aes()function nested within the chosengeomfunction - connected with the
+operator
Example: Scatterplot from Day 1
Task:
Create scatterplot of lifeExp against
gdpPercap from gapminder07 data.
Steps:
- Supply
gapminder07data frame as input toggplot()function - Choose a
geom; in this case we choosegeom_point()to generate points - Supply aesthetic mapping, i.e. specify
xandyvalues, togeom_point().
Example: Scatterplot from Day 1
Example: Scatterplot from Day 1
ggplot(gapminder07) +
geom_point(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
labs(title = "Relationship between life expectancy and GDP per capita in 2007",
x = "GDP per capita", y = "Life expectancy")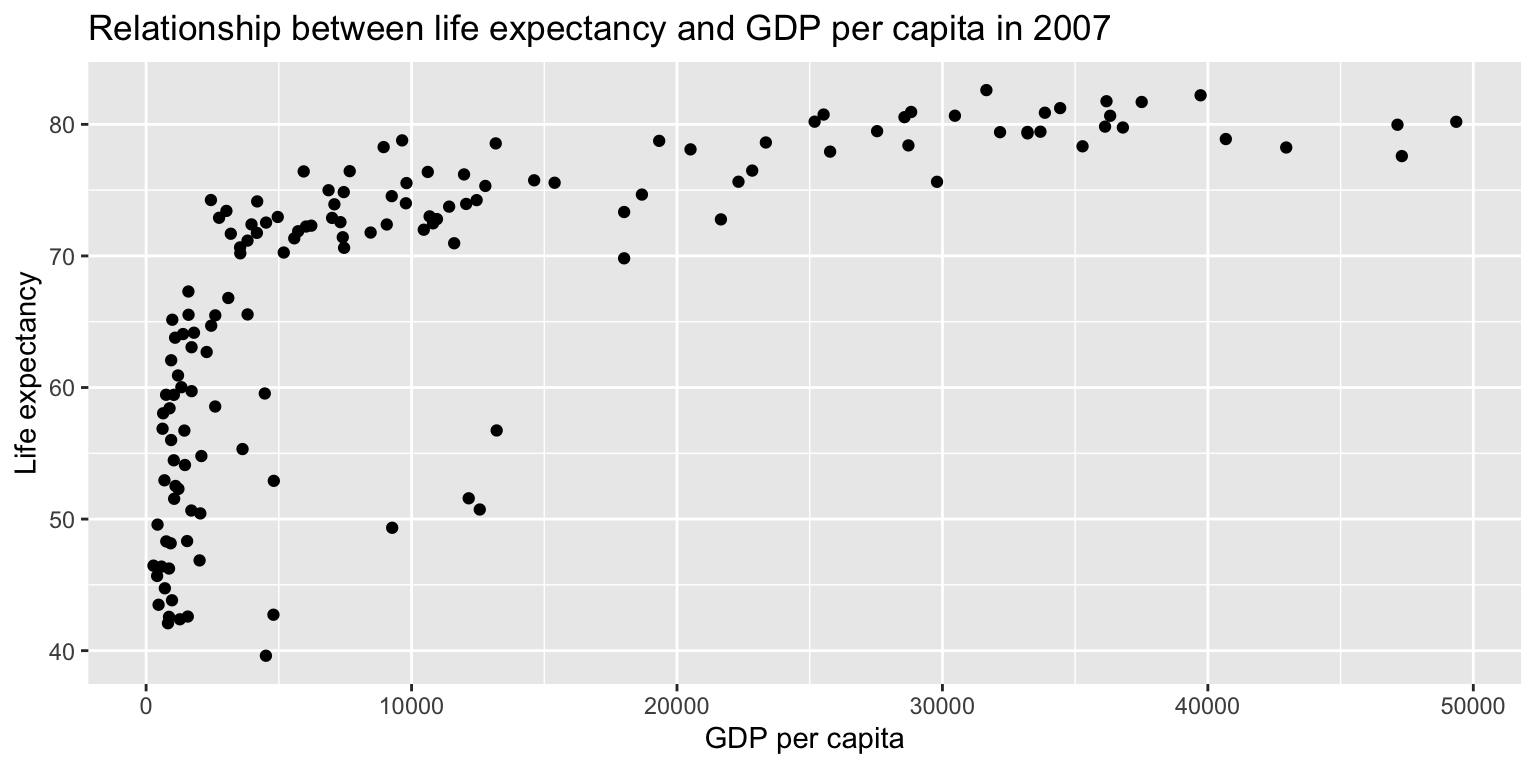
Exercise 1: Scatterplot
Using the gapminder07 data, create a scatterplot of the
natural log of gdpPercap as a function of the natural log
of pop. Give it a title and axis labels.
Remember, you will need three functions: ggplot(),
geom_point(), and labs().
Exercise 1: Scatterplot
ggplot(gapminder07) +
geom_point(aes(x = log(pop), y = log(gdpPercap))) +
labs(title = "Relationship between GDP per capita and population in 2007", x = "Logged GDP per capita", y = "Logged life expectancy")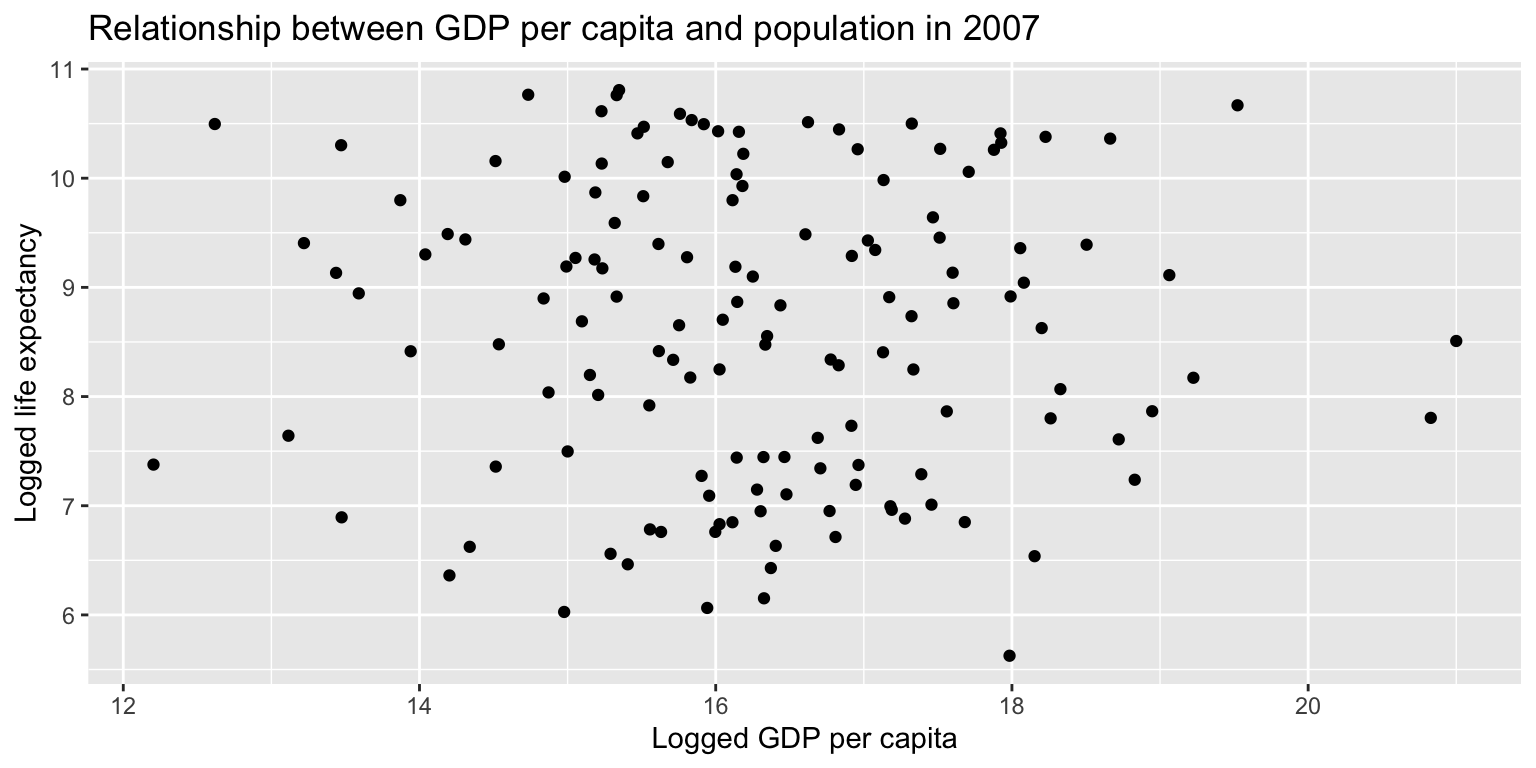
Preparing your data
- Recall the role of pipes (
%>%) indplyr. dplyrandggplot2are designed to work well together.- You can use a series of pipes to prepare your data before plotting.
- To see examples, let’s turn to the California energy data.
Example: Energy generated over time
Task:
Plot a column chart of total energy
generated over time.
Steps:
- Choose long-format generation data,
i.e.
long_gen. - Manipulate data frame to calculate total output per date-time.
- Pipe manipulated data frame into plot.
- Select
geom_col()and map appropriatexandyvariables.
Example: Energy generated over time
long_gen %>%
group_by(datetime) %>%
summarise(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=datetime, y=output)) +
labs(title="Total energy generated, by hour", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")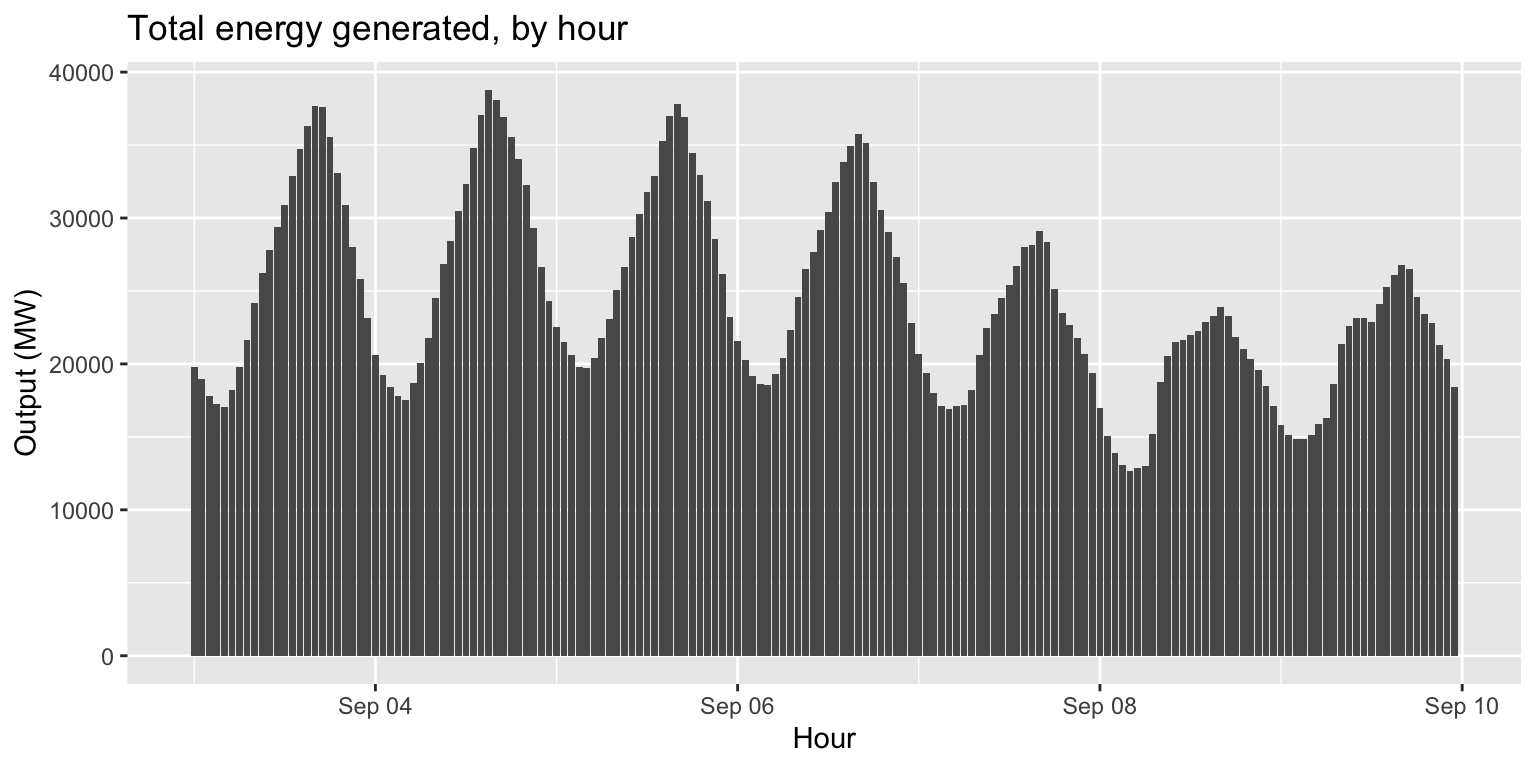
Exercise 2: Hydro power generated over time
Task:
Plot a column chart hydroelectric power generated
over time.
Hint: There are two types of hydroelectric sources in the
data: large_hydro and small_hydro.
Exercise 2: Hydro power generated over time
long_gen %>%
filter(source=="large_hydro"|source=="small_hydro") %>%
group_by(datetime) %>%
summarise(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=datetime, y=output)) +
labs(title="Total hydro power generated, by hour", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")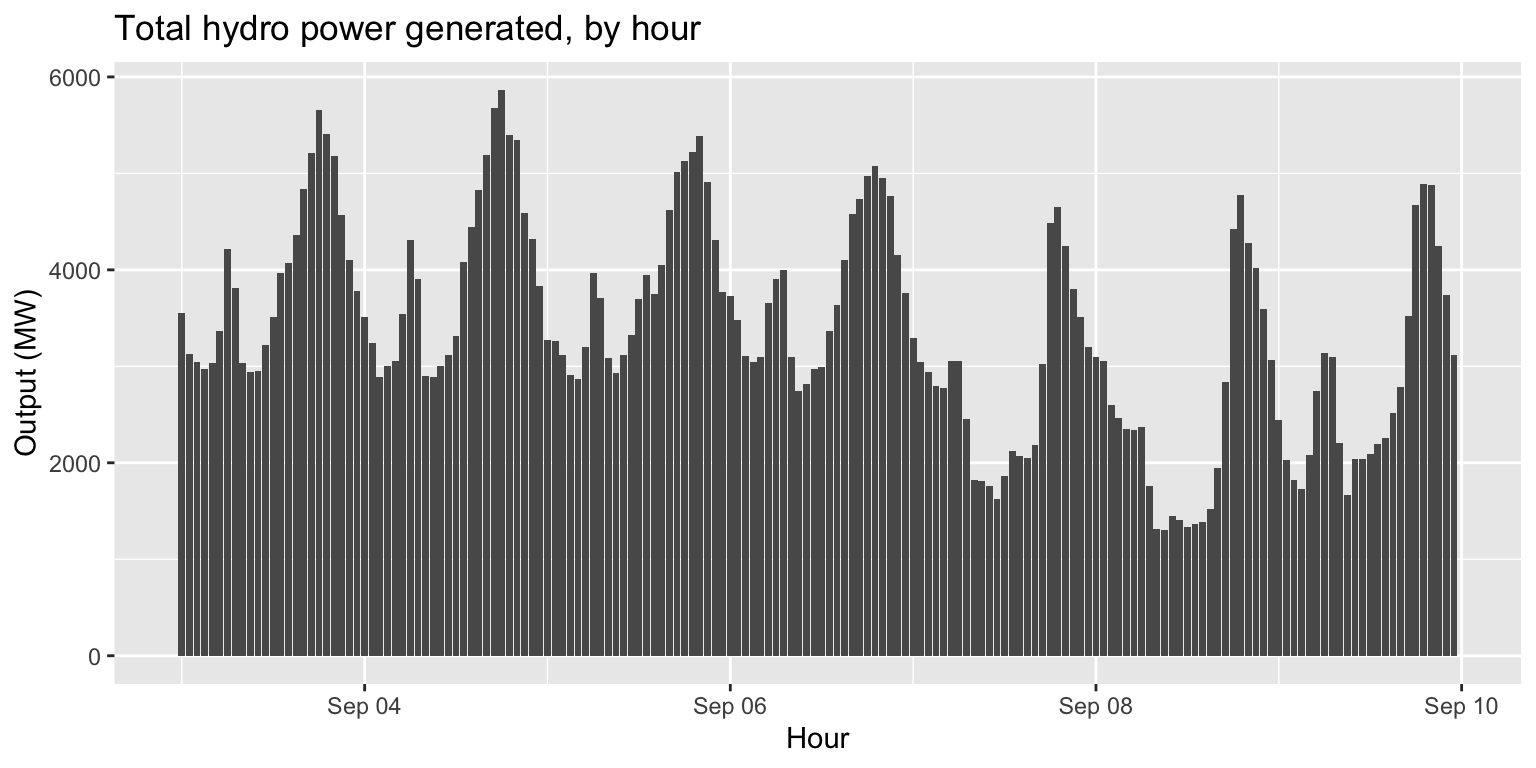
Exercise 2: Hydro power generated over time
generation %>%
mutate(hydro=large_hydro+small_hydro) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=datetime, y=hydro)) +
labs(title="Total hydro power generated, by hour", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")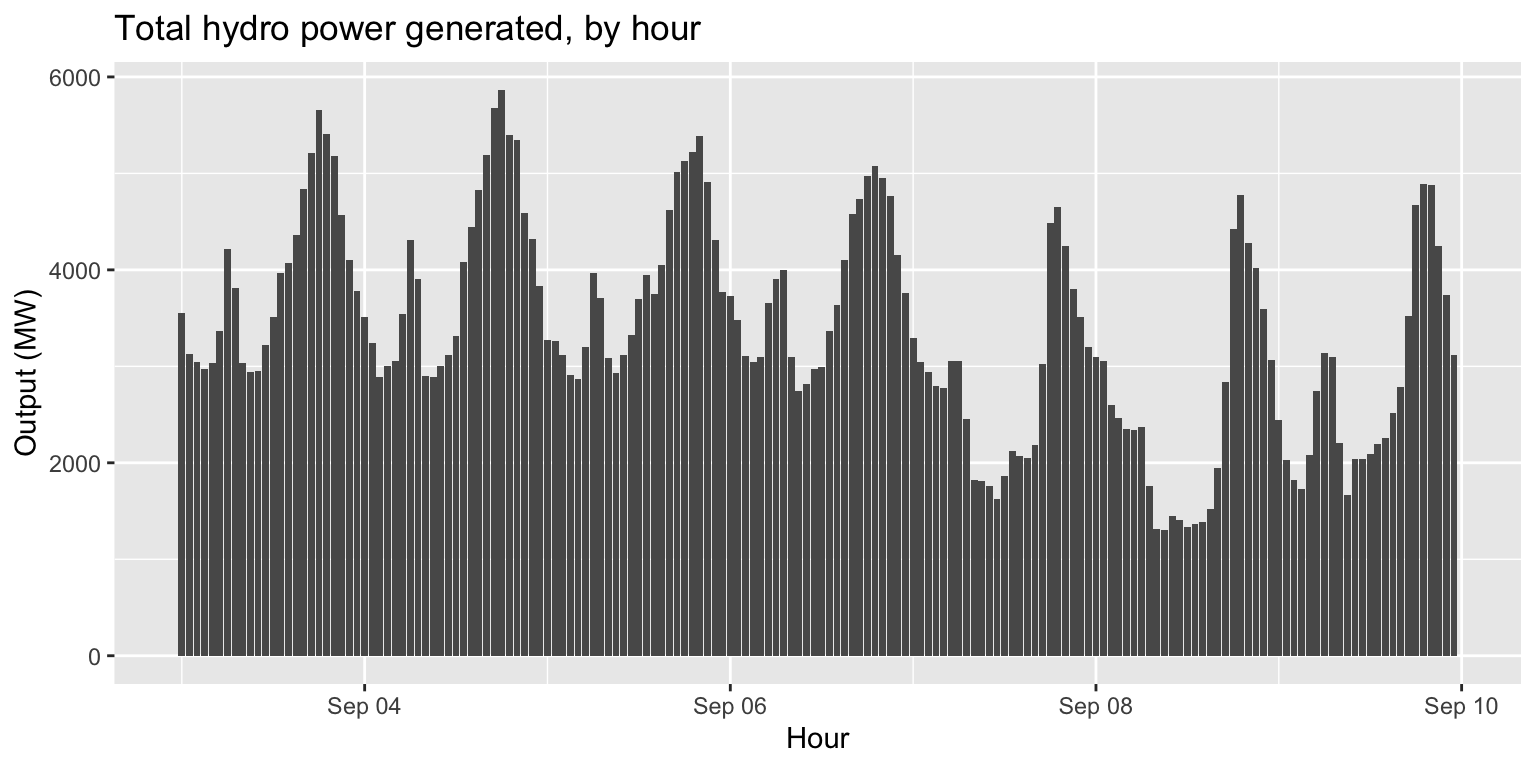
Geometric objects
We have already seen examples of two kinds of plots:
- Scatterplots, generated with
geom_point() - Column charts, generated with
geom_col()
Let’s see a few more.
Line plots: geom_line()
imports %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=imports)) +
labs(title="Energy imports over time", x="Hour", y="Amount imported (MW)")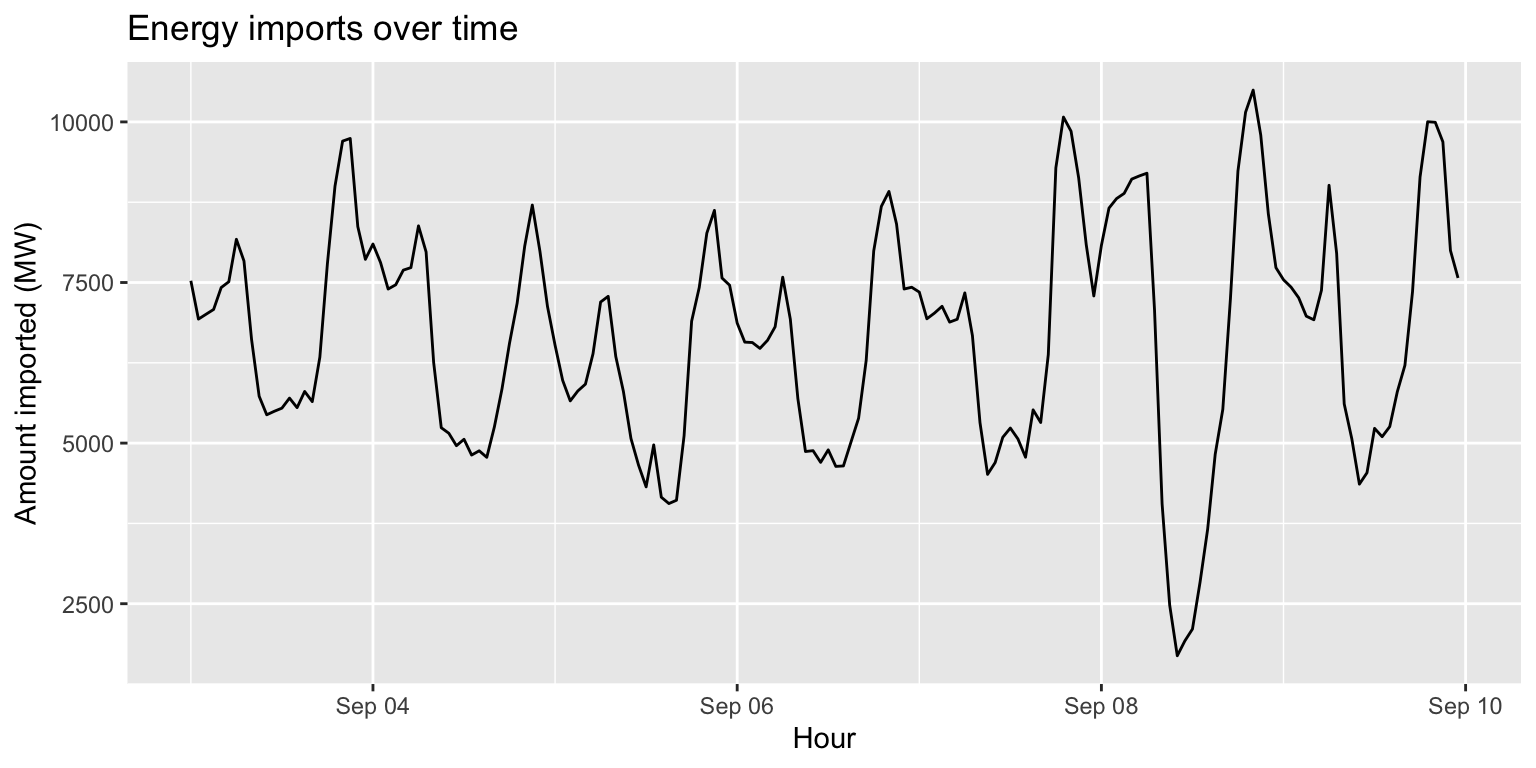
Interlude: changing geom characteristics
- In the geom functions, we have only been supplying
aesthetic mapping (in
aes()). - Geom functions can also control characteristics of
the geom object, outside the
aes()function. - In most geoms, we can modulate
size=andcol=. - Let’s try it with the line plot we just made.
Interlude: changing geom characteristics
imports %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=imports), size=1.2, col="red") +
labs(title="Energy imports over time", x="Hour", y="Amount imported (MW)")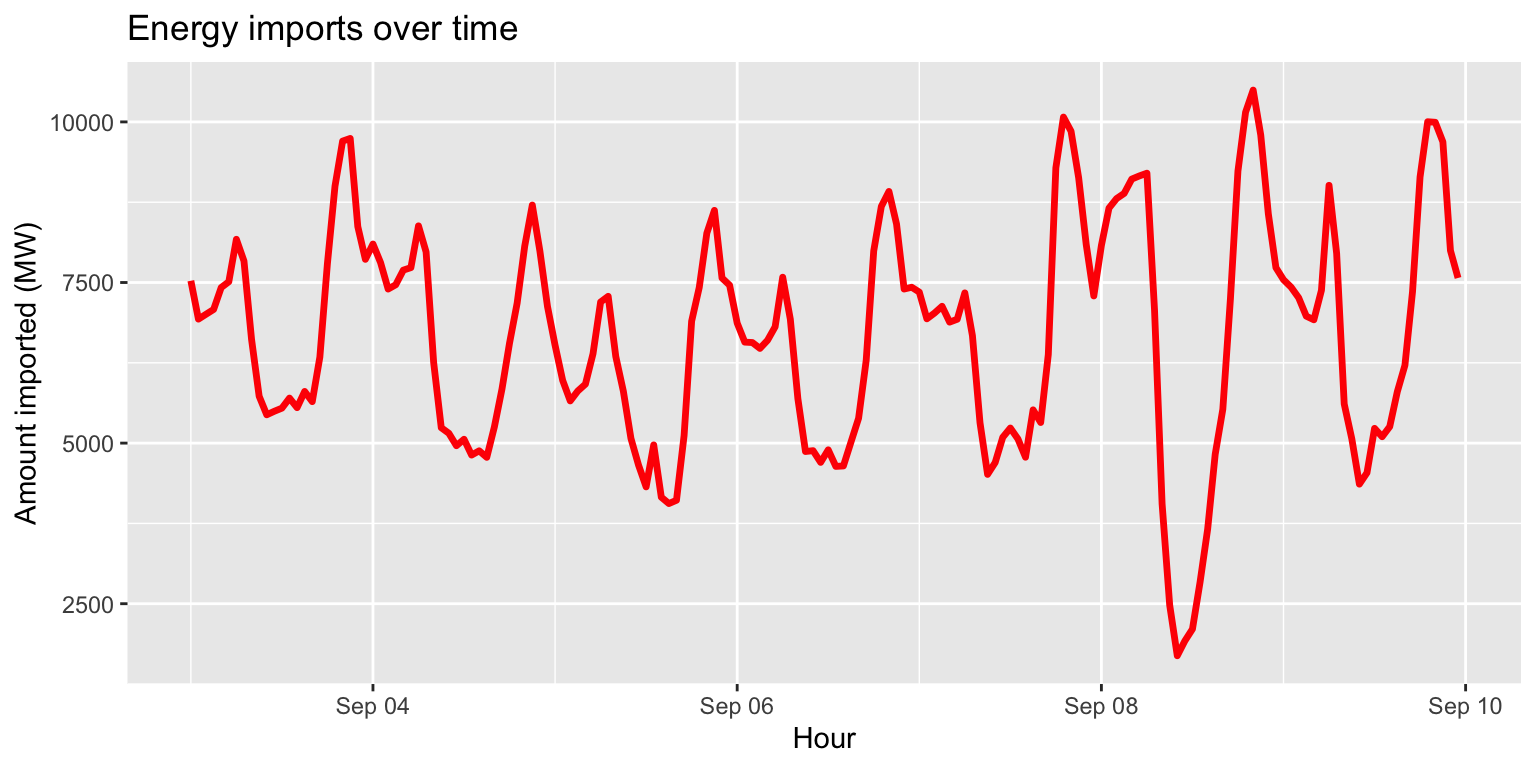
Area plots: geom_area()
generation %>%
ggplot() +
geom_area(aes(x=datetime, y=wind), fill="darkblue") +
labs(title="Hourly wind power generation, Sept 3-9", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")
Box plots: geom_boxplot()
long_gen %>%
ggplot() +
geom_boxplot(aes(x=source, y=output)) +
labs(title="Amount of energy generated by each source, Sept 3-9", x="Source type", y="Output (MW)")
Multiple geoms in one plot
Task:
Plot a line of large hydro generation over time,
and a smoothed line of the same relationship on top of it.
Steps:
- Supply the
generationdata toggplot(). - Create a line with
geom_line()with appropriatexandyaesthetics. Make it turquoise for fun. - Create a smoothed line with
geom_smooth()with the samexandyaesthetics.geom_smooth()plots smoothed conditional means (estimated using a loess regression)
Multiple geoms in one plot
generation %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=large_hydro), col="turquoise3") +
geom_smooth(aes(x=datetime, y=large_hydro)) +
labs(title="Hydroelectric (large) generation per hour, Sept 3-9", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess' and formula = 'y ~ x'
Exercise 3: Total output per source
Task:
Create a column chart that shows the total output per
source.
- Change the color of the columns to
"darkred". - Add a horizontal line indicating the mean output across all sources.
Use the cheatsheet to identify the
geomfunction that you need. - Add a meaningful title and axis labels using
labs().
Exercise 3: Total output per source
long_merged_energy %>%
group_by(source) %>%
summarise(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=source, y=output), fill="darkred") +
geom_hline(aes(yintercept=mean(output))) +
labs(title="Total output per energy source over Sept 3-9", y="Output (MW)", x="Source")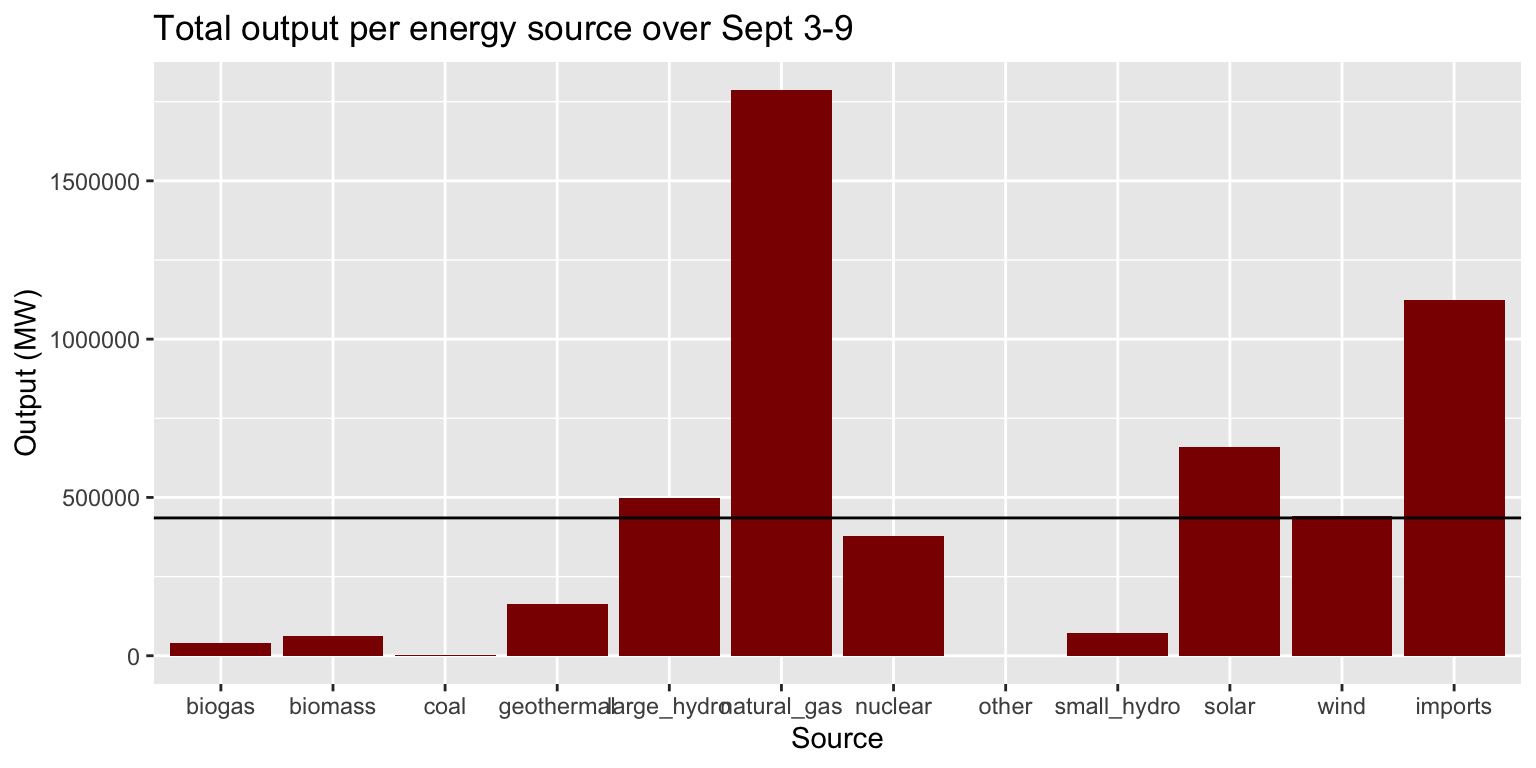
Additional layers
Labels
- We have already seen that the
labs()layer can add titles (title=) and axis labels (x=andy=) to a plot. - It can also add subtitles (
subtitle=) and captions (caption=).
Labels
imports %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=imports), col="red") +
labs(title="Energy imports over time in California", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018",
caption="Source: California Energy Commission", x="Hour", y="Amount imported (MW)")
Scales
- Scales allow you to manipulate the relationship
between data values and aesthetics beyond aesthetic mapping.
- AKA: scales “control the details of how data values are translated to visual properties” (quote from reference guide).
- For example:
scale_alpha: control transparency settingsscale_colorandscale_fill: control color palettes and other aspects of data mapped to colorsscale_xandscale_y: control the position of axis markers
- The cheatsheet is your friend!
Scales
Task:
Recreate line plot of imports over time, but label x-axis
with hours rather than dates.
Steps:
- Check the cheatsheet!
- Supply
importsdata toggplot(). - Add a
geom_line()layer and map appropriatexandyvariables. - Add a
scale_x_datetime()layer and usedate_labels=anddate_breaks=arguments to modify x-axis labels and breaks. - Add a
labs()layer.
Example: Imports over time
imports %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=imports), col="red") +
scale_x_datetime(date_labels="%H:%M", date_breaks="12 hours") +
labs(title="Energy imports over time in California", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Amount imported (MW)")
Themes: presets
ggplot comes with several preset themes that can be added as layers, including:
theme_grey(): defaulttheme_bw(): strip colors, including grey gradientstheme_dark()andtheme_light(): change the background of the coordinate systemtheme_minimal()andtheme_void(): see reference guide for details
Example: Imports over time
imports %>%
ggplot() + geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=imports), col="red") +
scale_x_datetime(date_labels="%H:%M", date_breaks="12 hours") +
labs(title="Energy imports over time in California", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Amount imported (MW)") +
theme_minimal()
Themes: manual
The theme() layer lets you modulate many components of
the theme, including:
- Angle, position, and other characteristics of axis
labels (e.g.
axis.labels.x =). - Angle, position, and other characteristics of
legends (e.g.
legend.position =). - Characteristics of the background of the plot
(e.g.
plot.background =). - For a full list of the components that can be
modified, see the help file for
ggplot2::theme().
Example: Imports over time
imports %>%
ggplot() + geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=imports), col="red") +
scale_x_datetime(date_labels="%H:%M", date_breaks="12 hours") +
labs(title="Energy imports over time in California", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Amount imported (MW)") +
theme(axis.text.x=element_text(angle=45, hjust=1, size=12))
Coordinate system adjustment
coord_flip()is the default Cartesian coordinate system used; by explicitly calling this function, you can change the limits of thexandyaxes from their defaultscoord_fixed()sets a fixed aspect ratio between thexandyaxescoord_transform()lets you transform the Cartesian coordinates using functions likesqrtorlogcoord_polar()changes the coordinate system to polar coordinates rather than a Cartesian system
Example: coord_flip()
long_gen %>%
mutate(date=lubridate::date(datetime)) %>%
group_by(date) %>% summarise(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() + geom_col(aes(x=date, y=output)) +
labs(title="Total energy generated, by day", x="Day", y="Output (MW)")
Example: coord_flip()
long_gen %>%
mutate(date=lubridate::date(datetime)) %>%
group_by(date) %>% summarise(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() + geom_col(aes(x=date, y=output)) +
labs(title="Total energy generated, by day", x="Day", y="Output (MW)") +
coord_flip()
Stats
- There are several
statfunctions in ggplot that enable you to conduct statistical transformations of your data prior to plotting. statandgeomlayers can be used interchangeably, as eachstatlayer has ageomargument and vice versa.- You may want to use stat layers or arguments to override default settings, or to use transformed versions of a variable in your plot.
- For more, see Chapter 3.7 of the R for data science online textbook.
Visualizing grouped data
- We often want to visualize multiple variables, or a variable that can be divided into groups, in one graphic.
- There are two broad principles for visualizing
grouped variables in R:
- Identify a grouping variable in a
geom()using thegroup =argument, and demarcate the distinct objects created per group in some way. - Use facets to generate geometric objects in separate coordinate systems for each group.
- Identify a grouping variable in a
Colors and fill
Task:
Create a line plot of energy output over time, with separate
lines for each source.
Steps:
- Supply the data frame
long_merged_energytoggplot(). - Add a
geom_line()layer and specifyx=datetimeandy=output. - Also specify that
group=sourceandcol=source. - Add a
labs()layer.
Colors and fill
long_merged_energy %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=output, group=source, col=source)) +
labs(title="Output by energy source over time", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")
Exercise 4: Colors and fill
Task:
Create a line plot that compares generation of wind, solar,
and geothermal energy over time.
Bonus: Set the line size to 1.5.
Exercise 4: Colors and fill
long_merged_energy %>%
filter(source=="wind"|source=="solar"|source=="geothermal") %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=output, group=source, col=source), size=1.5) +
labs(title="Wind vs. Solar vs. Geothermal generation", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")
Customizing with scale_color layers
long_merged_energy %>% filter(source=="wind"|source=="solar"|source=="geothermal") %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=output, group=source, col=source), size=1.5) +
scale_color_brewer(palette="Accent", name="Energy source") +
labs(title="Wind vs. Solar vs. Geothermal generation", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")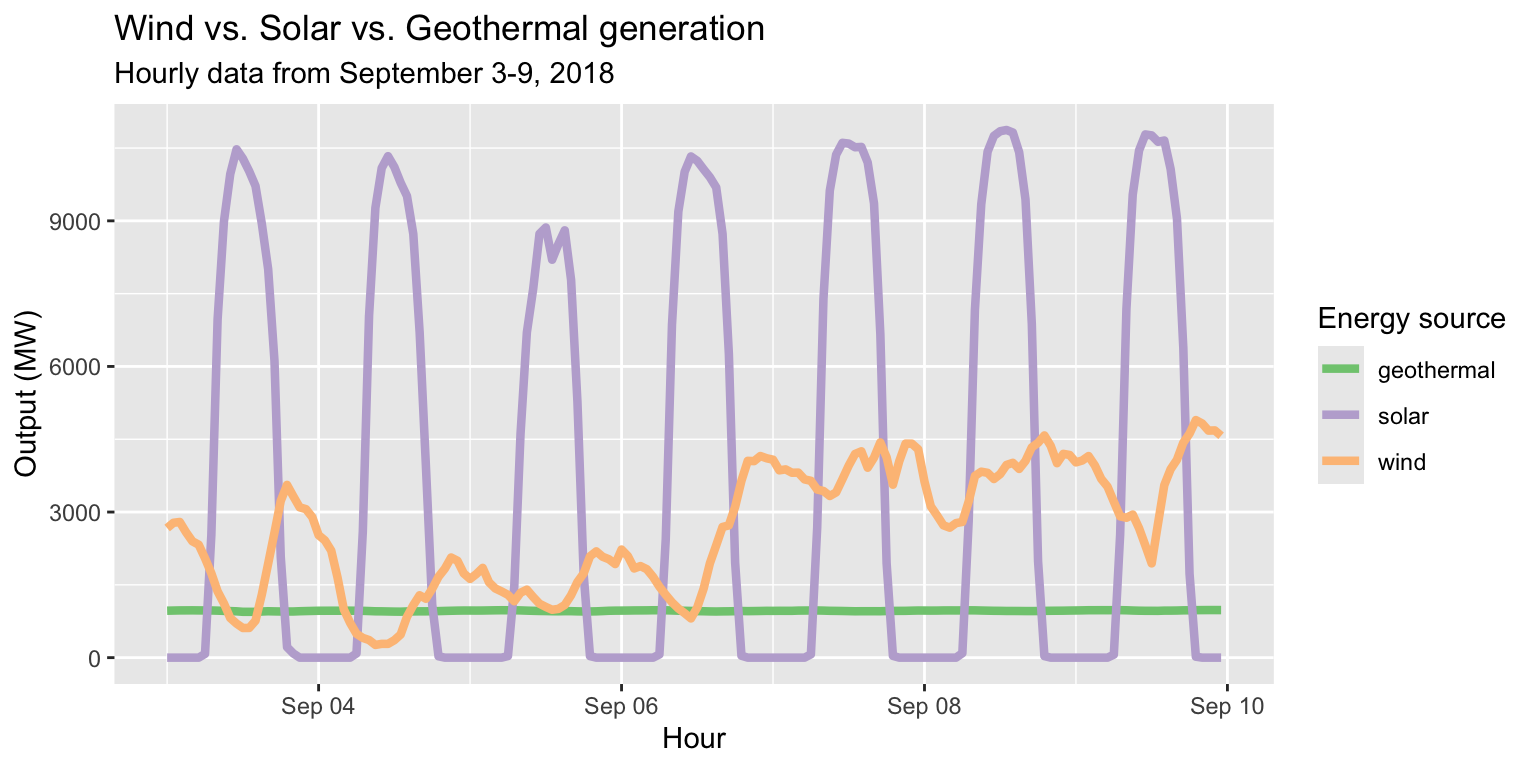
Colors and fill
col=is used to color objects like lines and pointsfill=is used to color objects like columns and histogramscol=will create colored outlines for such objects
- After some trial and error, this will become intuitive
Position adjustment
- Once we introduce a grouping variable to a
geomfunction, we generate multiple geometric objects on the same plot. - Colors and fill help us distinguish each object from other objects.
- Another way to distinguish objects, often used together with color/fill, is position adjustment.
Example: Energy use by day
Task:
Create a column chart of energy use by day, grouped by
source.
Steps:
- Modify
long_merged_energyto summarize output by date and source.- Use
mutate()to create adatevariable fromdatetime. - Use
group_by()andsummarize()to calculate total output per date per source.
- Use
- Supply modified data frame to
ggplot() - Add a
geom_col()layer, supplyxandyaesthetics. - Specify
group=sourceandfill=source. - Add a
labs()layer.
Example: Energy use by day
long_merged_energy %>%
mutate(date=lubridate::date(datetime)) %>%
group_by(date, source) %>%
summarize(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=date, y=output, group=source, fill=source)) +
labs(title="Energy use by day", x="Day", y="Output (MW)")## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'date'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.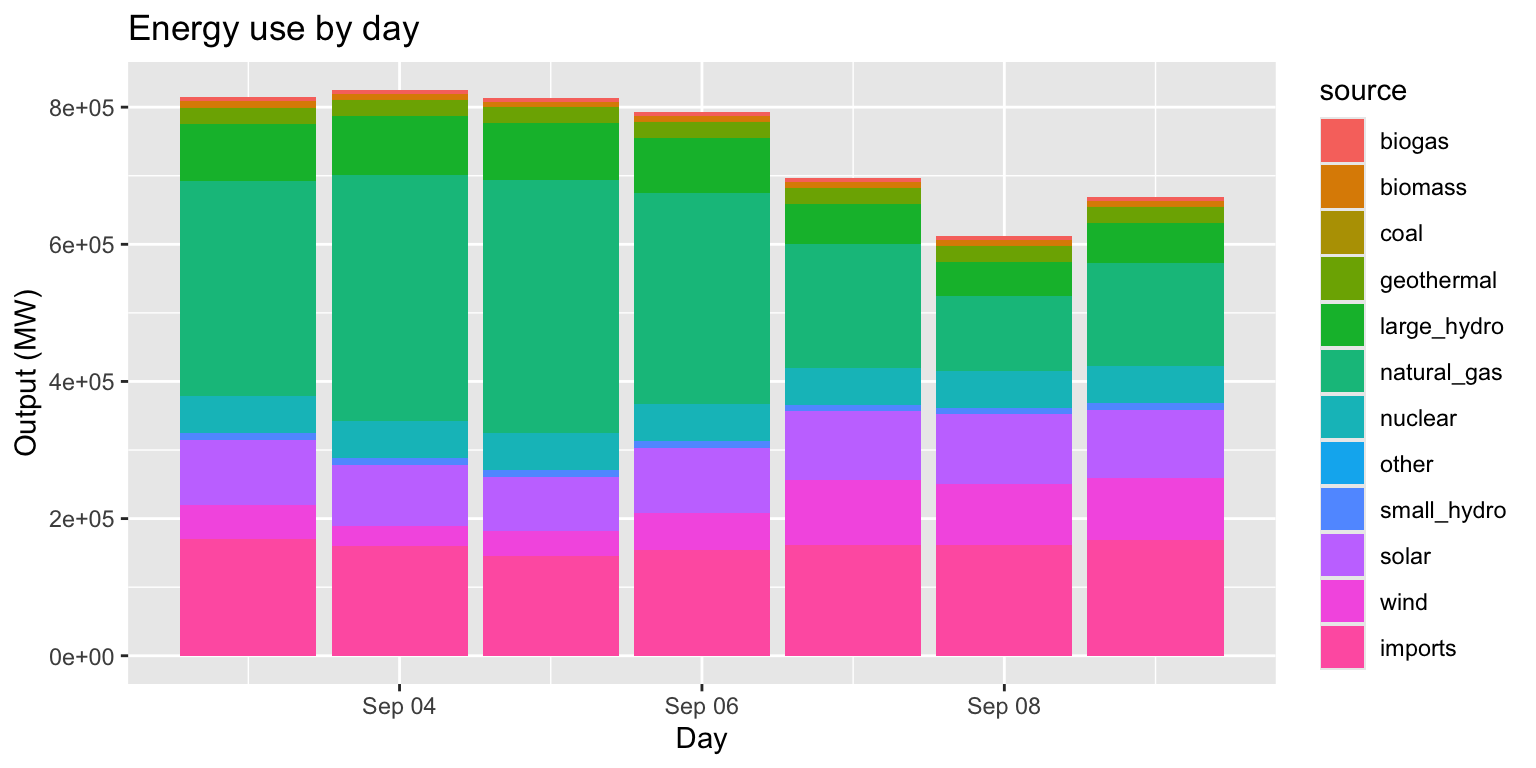
Example: Energy use by day
- This column chart is useful if our main goal is to examine total output over time across sources.
- But what if our main goal is to compare trends
across sources?
- We can use
position="dodge"ingeom_col()‘unstack’ the columns for each source.
- We can use
- What if our goal is to compare what portion of
output per day each source comprises?
- We can use
position="fill"to normalize height of stacked columns.
- We can use
Example: Energy use by day (pos dodge)
long_merged_energy %>%
mutate(date=lubridate::date(datetime)) %>%
group_by(date, source) %>%
summarize(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=date, y=output, group=source, fill=source), position="dodge") +
labs(title="Energy use by day", x="Day", y="Output (MW)")## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'date'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.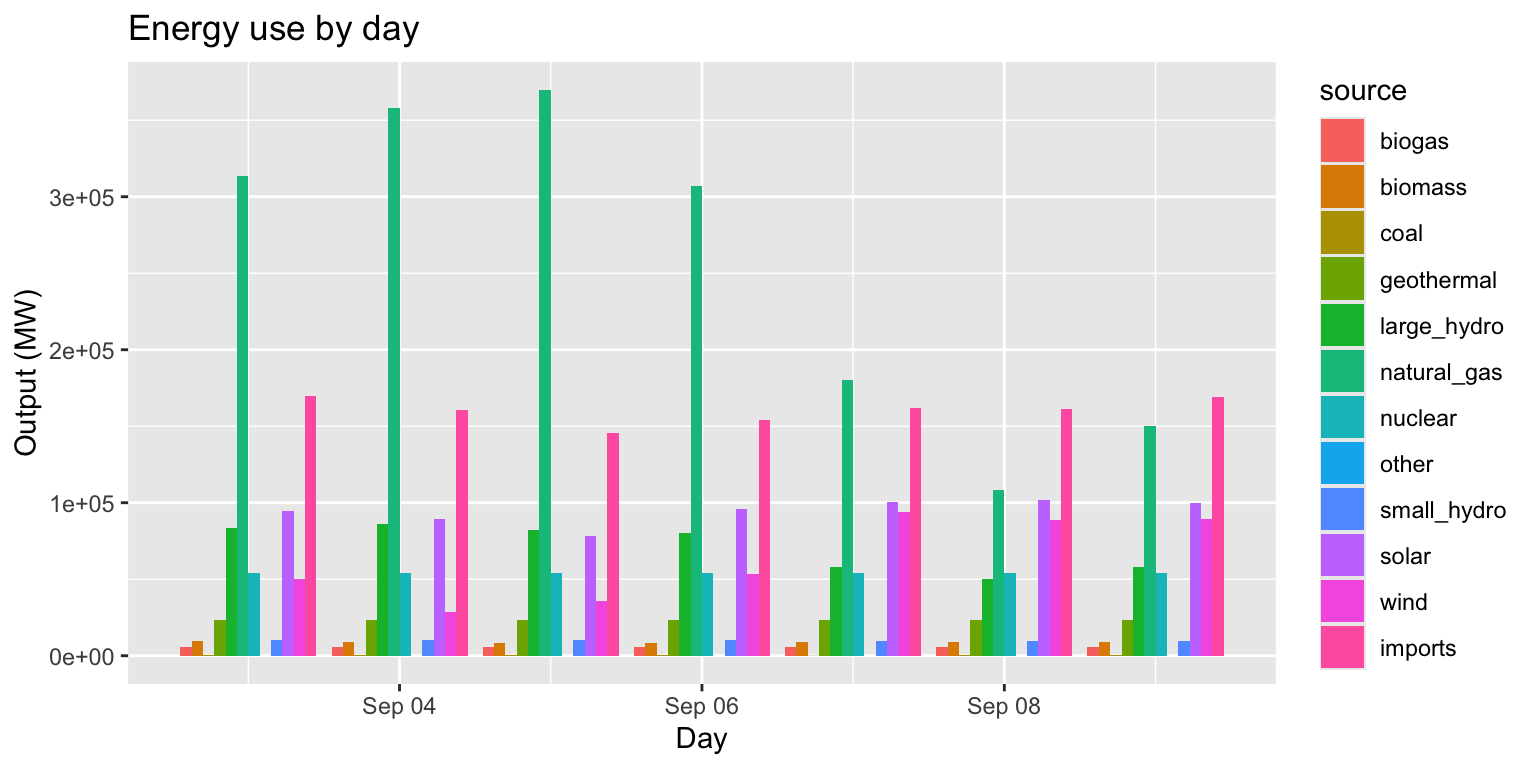
Example: Energy use by day (pos fill)
long_merged_energy %>%
mutate(date=lubridate::date(datetime)) %>%
group_by(date, source) %>%
summarize(output=sum(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_col(aes(x=date, y=output, group=source, fill=source), position="fill") +
labs(title="Energy use by day", x="Day", y="Output (MW)")## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'date'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.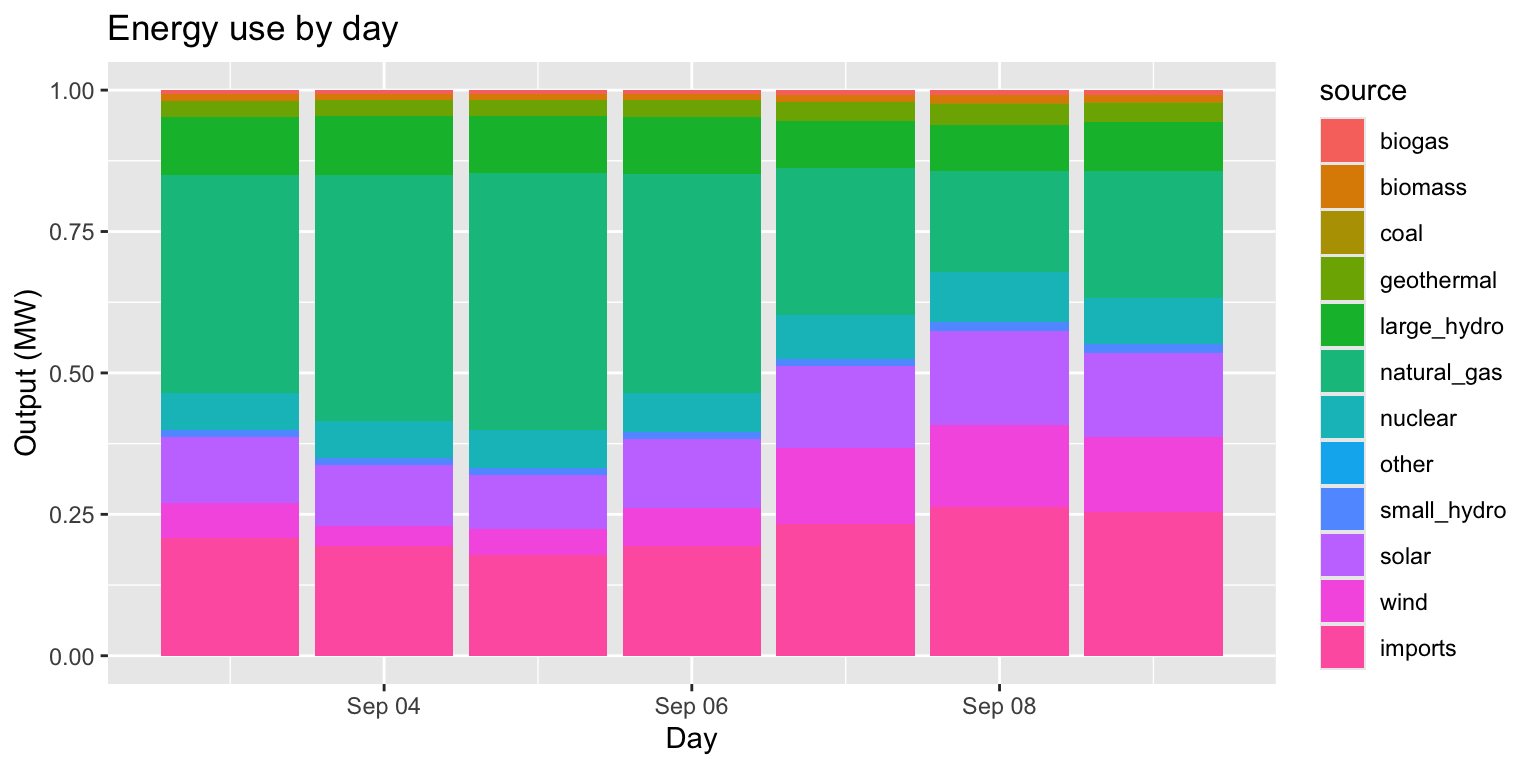
Shapes and linetypes
- Colors/fill and position adjustment are the most common and intuitive way to distinguish geometric objects from each other.
- Shapes and linetypes are two other ways.
- The idea here is to modify what the object actually looks like.
Example: Energy source group, by day
Task:
Create a line graph of the output by day, with a different
line for each regrouped group (renewable, hydro, etc.)
Steps:
- Prepare data frame that summarizes output by date
and “group” from
regroup. - Supply modified data frame to
ggplot(). - Two choices!
- Add
geom_line()andgeom_point()withshape=group. - Add
geom_line()withlinetype=group.
- Add
Example: Energy source group by day
# Prepare data
long_merged_energy_regroup <- long_merged_energy %>%
rename(type = source) %>%
merge(regroup, by = "type") %>%
mutate(date=lubridate::date(datetime)) %>%
group_by(date, group) %>%
summarise(output=sum(output))## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'date'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.## # A tibble: 6 × 3
## # Groups: date [1]
## date group output
## <date> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 2019-09-03 hydro 93919.
## 2 2019-09-03 imports 169826.
## 3 2019-09-03 nuclear 53926.
## 4 2019-09-03 other 0
## 5 2019-09-03 renewable 183304.
## 6 2019-09-03 thermal 313436.Example: Energy source group, by day
long_merged_energy_regroup %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=date, y=output, group=group, col=group), size=0.8) +
geom_point(aes(x=date, y=output, group=group, shape=group)) +
labs(title="Output by source group over time", subtitle="Data collected during September 3-9, 2018", x="Date", y="Output (MW)")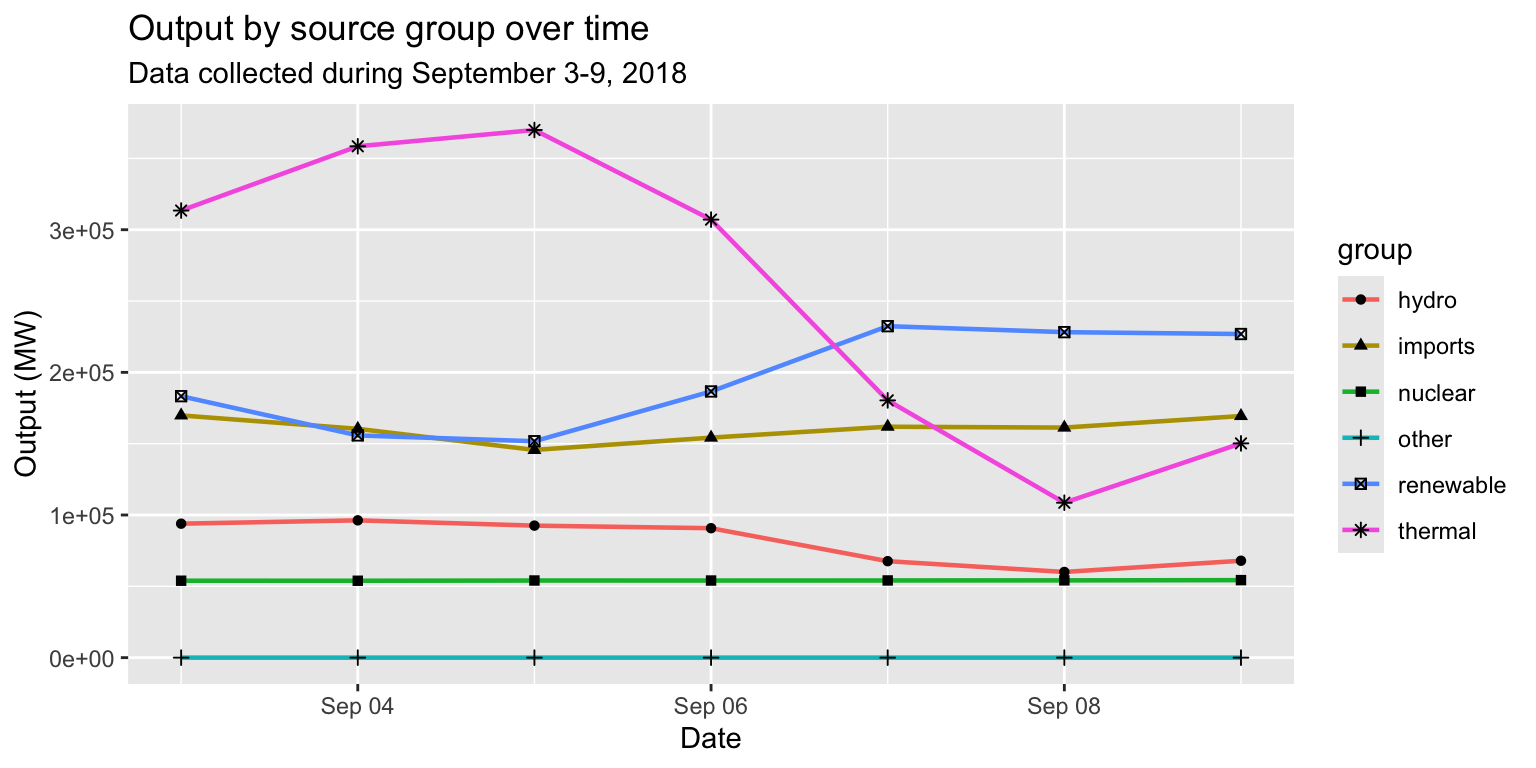
Example: Energy source group, by day
long_merged_energy_regroup %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=date, y=output, group=group, linetype=group), size=1) +
labs(title="Output by source group over time", subtitle="Data collected during September 3-9, 2018", x="Date", y="Output (MW)")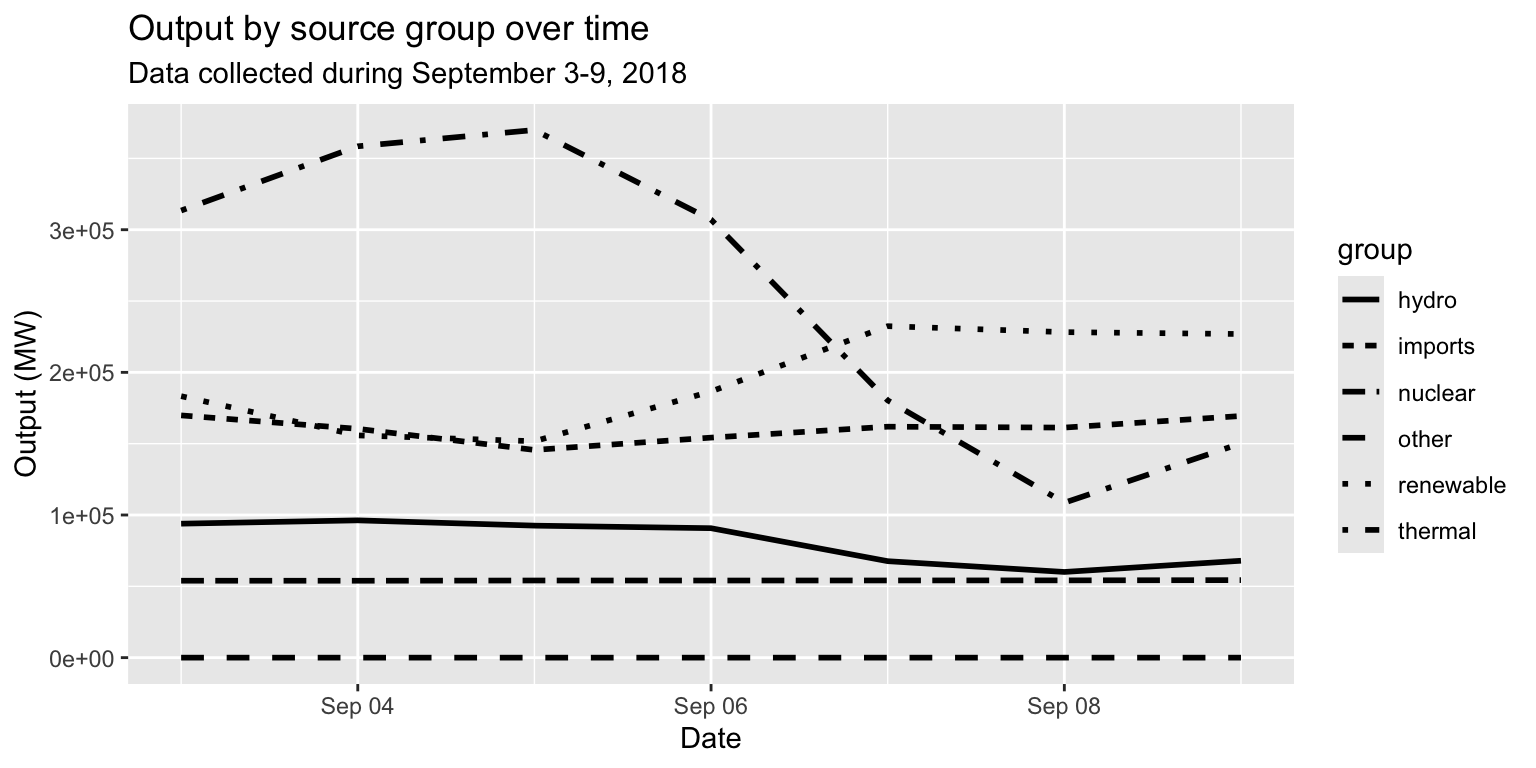
Sizes and alpha
size=andalpha=insideaes()modulate the size and transparency of geom objects based on some data value.- They are particularly useful when you want to distinguish objects based on some continuous variable.
- Let’s return to the Gapminder data for an example.
Example: Life expectancy over GDP
gapminder07 %>%
ggplot() +
geom_point(aes(x=log(gdpPercap), y=lifeExp, size=pop, col=continent)) +
scale_size_continuous(name="Population") + scale_color_discrete(name="Continent") +
labs(title="Life expectancy as a function of GDP per capita in 2007", x="Logged GDP per capita", y="Life expectancy")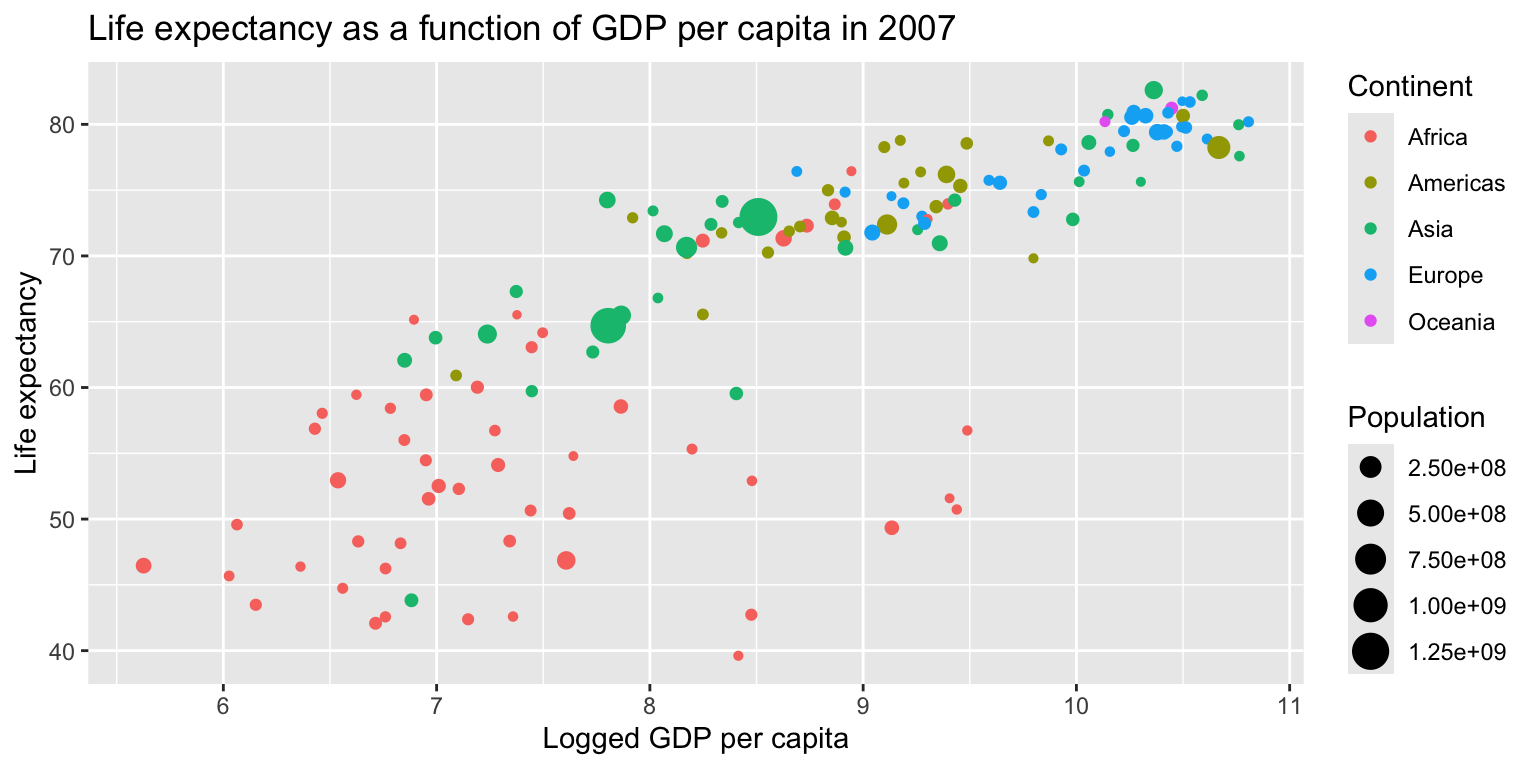
Exercise 5: Average hourly output by source
Task:
Visualize the average output for each hour of the day,
grouped by source.
You need to identify the output per source per hour (e.g. 01:00, 02:00, etc) averaged over all days.
- You will need to prepare your data using both
dplyrandlubridatefunctions. - You can choose which
geom(s) to use, and how to demarcate groups. - Bonus: use a scale layer to set a color palette (try
"Set3") and change the legend name. - Remember to add
labs()!
Exercise 5: Average hourly output by source
ex5 <- long_merged_energy %>%
mutate(hour=lubridate::hour(datetime)) %>%
group_by(hour, source) %>%
summarize(output=mean(output)) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_area(aes(x=hour, y=output, fill=factor(source))) +
scale_fill_brewer(palette="Set3", name="Source") +
labs(title="Average hourly output by source",
subtitle="Data collected during September 3-9",
x="Hour of the day", y="Output (MW)") +
theme_bw()## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'hour'. You can override using the
## `.groups` argument.Exercise 5: Average hourly output by source
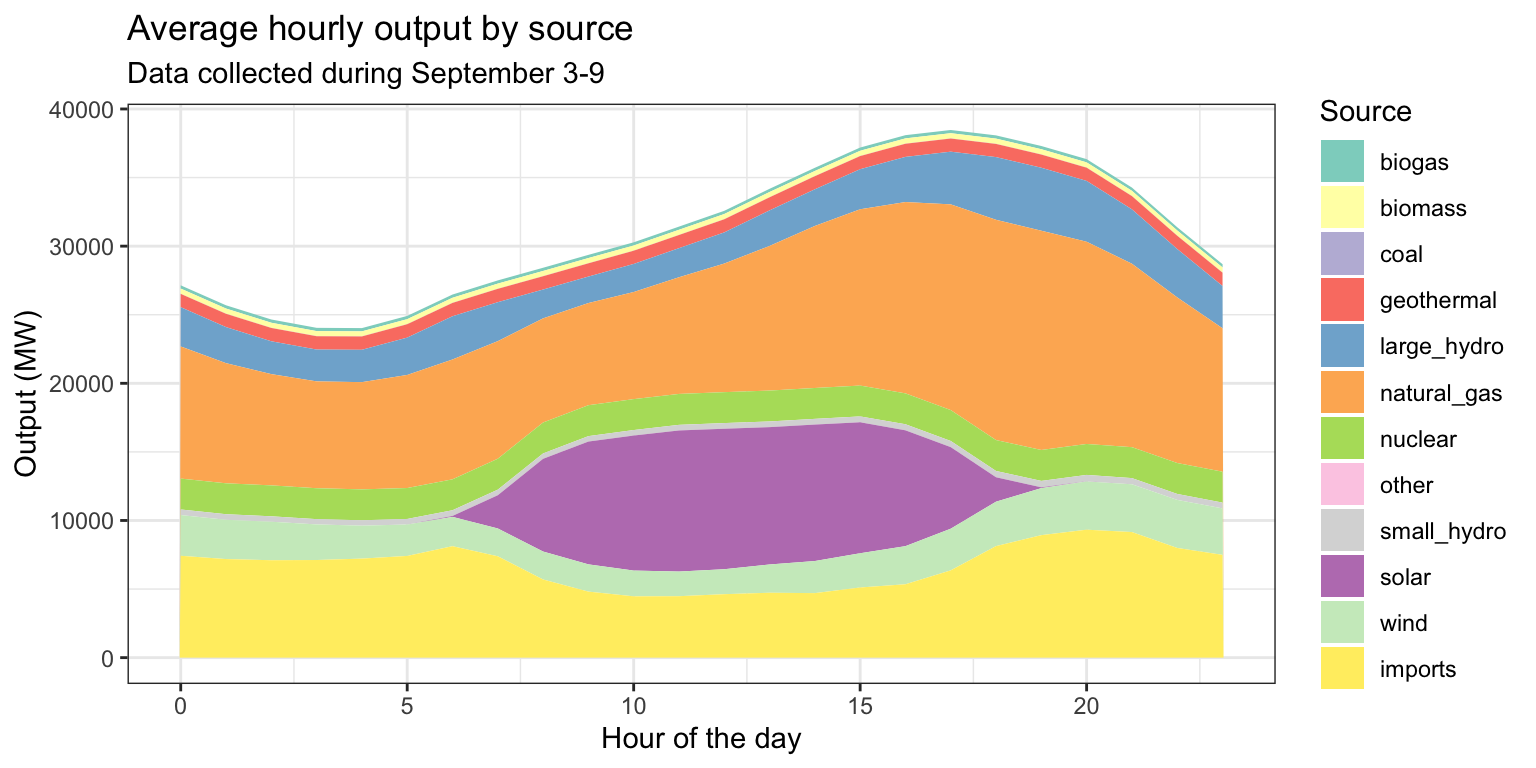
Facets
- So far we have been visualizing grouped data by changing the appearance or position of the objects.
- A different approach is to use facets, which creates separate coordinate systems for each geometric object.
Example: Comparing generation patterns
Task:
Compare energy generation over time, across sources.
How do we do this? Using what we’ve learned so far:
- Supply
long_gentoggplot(). - Add a
geom_line()layer, settingx=datetimeandy=outputinaes(). - Let’s set
group=sourceandcol=sourceinaes().
Example: Comparing generation patterns
long_gen %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x=datetime, y=output, group=source, col=source), size=1) +
labs(title="Generation over time, by energy source", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")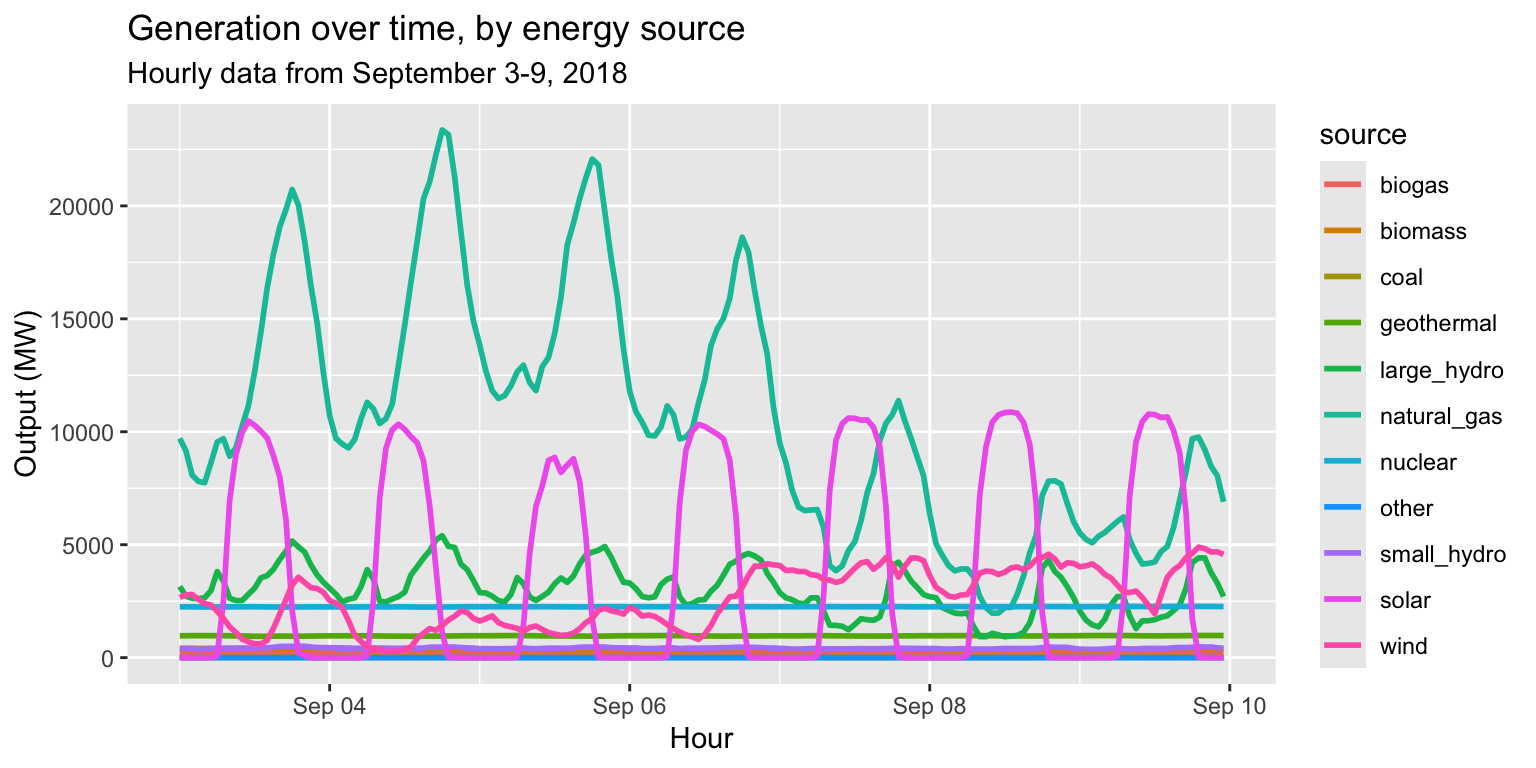
Example: Comparing generation patterns
Is this a helpful plot?
- Not if our goal is to compare the patterns of each source.
- It’s too noisy!
- Instead of setting
col=inaes(), let’s add afacet_wrap()layer. - Specifically,
facet_wrap(~source), i.e. tell ggplot to “facet by source”.
Example: Comparing generation patterns
long_gen %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x = datetime, y = output)) +
facet_wrap(~source) +
labs(title="Generation over time, by energy source", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")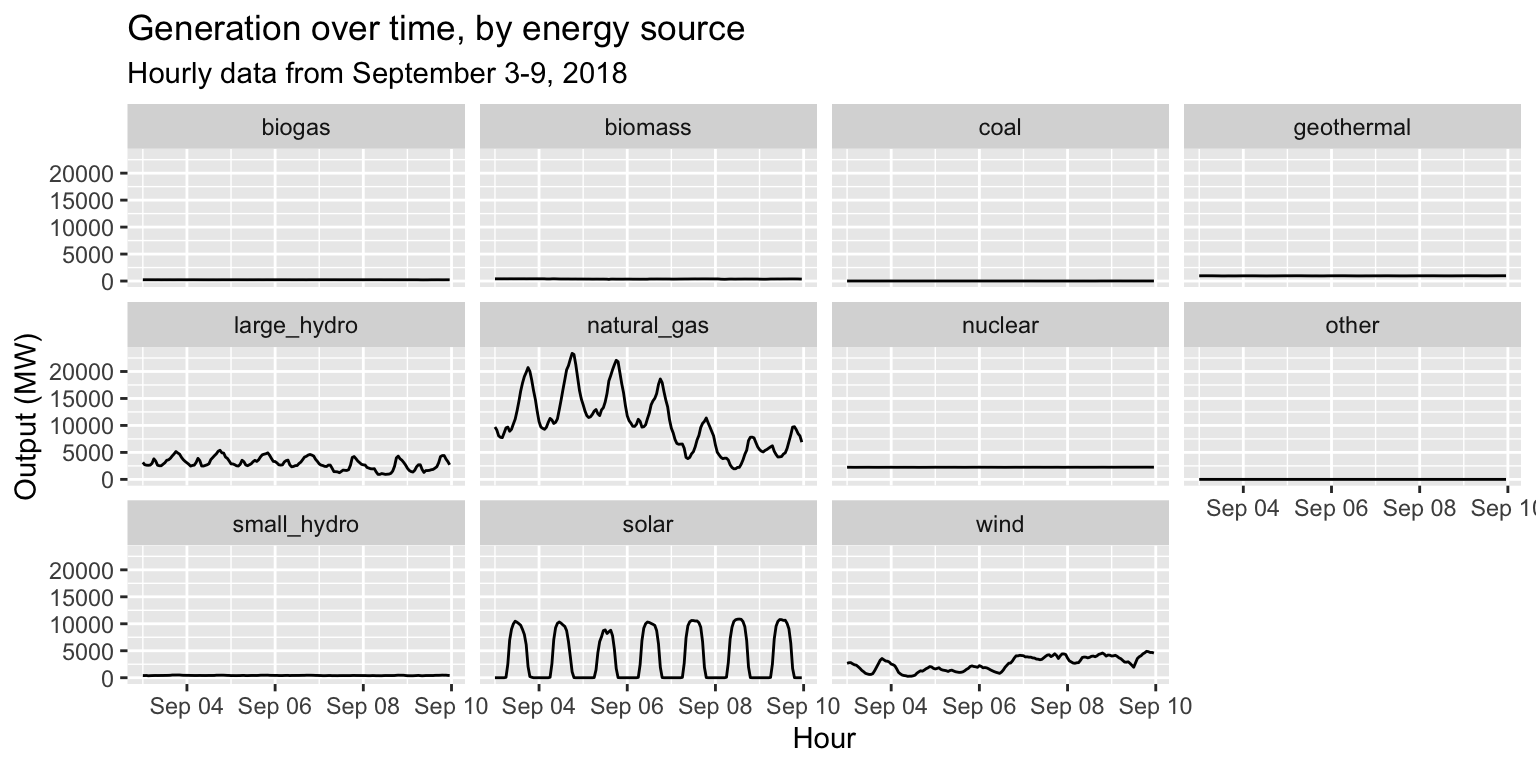
Example: Comparing generation patterns
long_gen %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x = datetime, y = output)) +
facet_wrap(~source, scales="free") +
labs(title="Generation over time, by energy source", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)")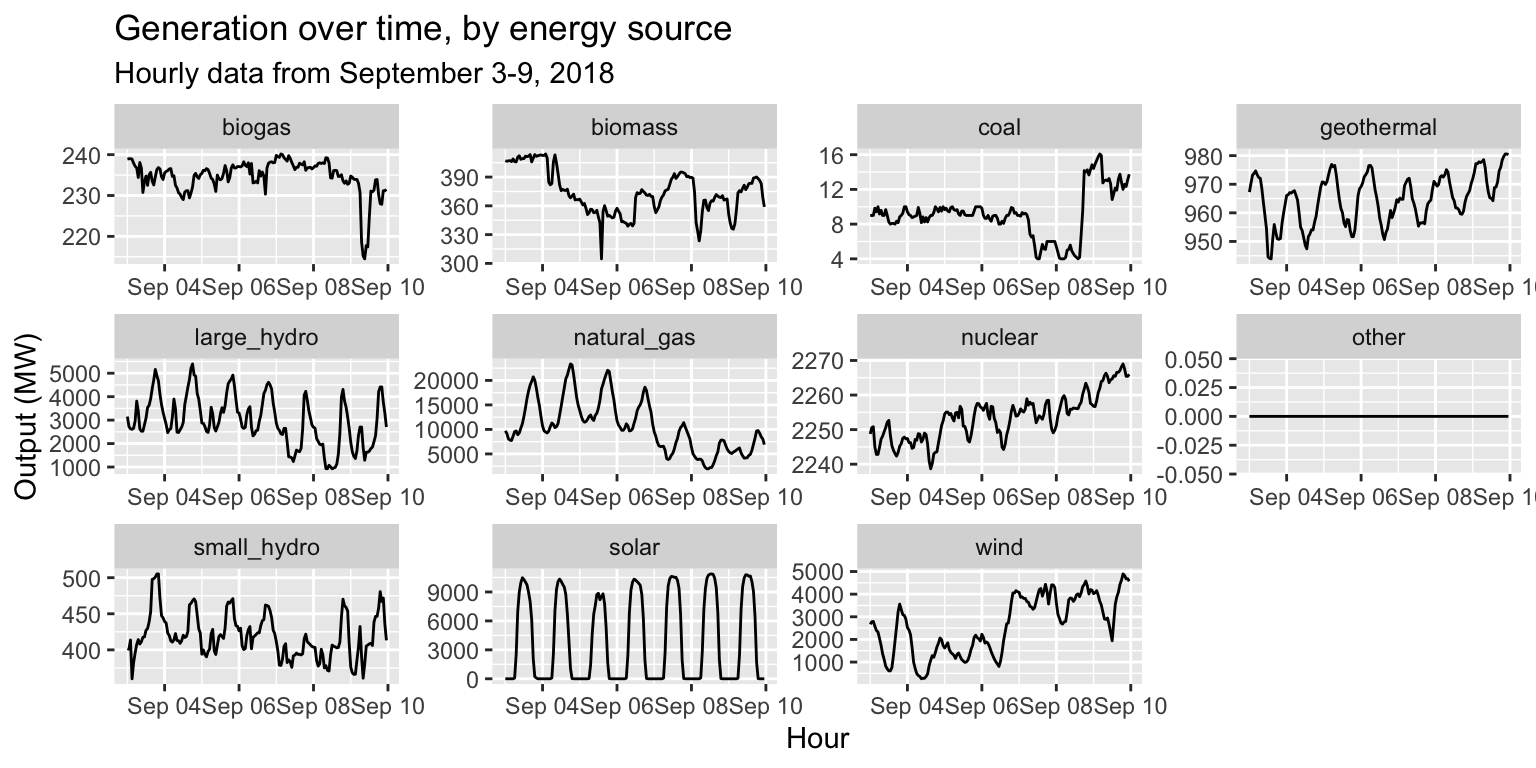
Exercise 6: Facets
Task:
Alter the facet plot by:
- Making the line in each plot a different color
- Making the lines thicker
- Moving the legend to the bottom
Exercise 6: Facets
long_gen %>%
ggplot() +
geom_line(aes(x = datetime, y = output, col=source), size=1) +
facet_wrap(~source, scales="free") +
labs(title="Generation over time, by energy source", subtitle="Hourly data from September 3-9, 2018", x="Hour", y="Output (MW)") +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")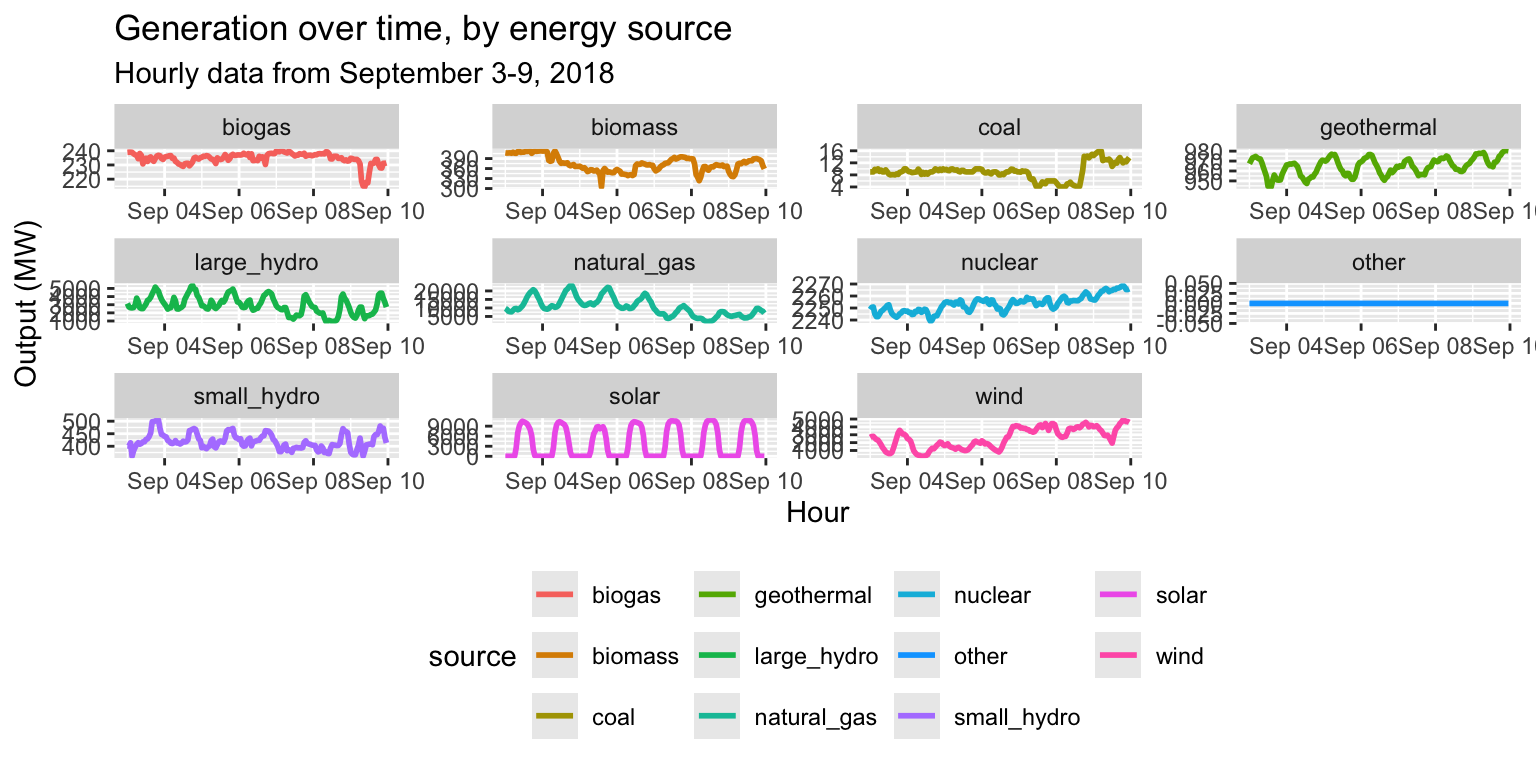
Final notes
Saving images
Three ways to save images created by ggplot:
- Assign the result of your ggplot code to a named object, which can be saved like other objects in your R workspace
- Use the “save” icon in the Plots tab of RStudio
- Add the function
ggsave()as a layer to your plotting code
Break!
This is the end of the R lecture sessions.
After a short break, we will return for a cumulative exercise that combines the skills you have learned since Monday.
Final Exercise
The instructions are in a markdown file in the exercises
folder. Create a new RMarkdown file (save it using this naming
convention: FinalRExercise_LastnameFirstname.Rmd), in which
you will complete the exercise.
You can work in small groups, but write up your code separately.
Raise your hand if you need help!
Optional Submissions
You’ve created several RMarkdown files over the past three days. Since you stored these in a forked repo, it is possible to create a pull request and ‘submit’ these changes to the base repo. This is optional, but gives you a chance to explore Github functionality and share your work with your classmates.
Before you submit your completed exercises, move every new file
in your repo to the submissions folder. This
ensures that we won’t inadvertently make changes to the session
materials. Then, create a new pull request, asking to merge changes from
your fork to the base repository.
Comment your code
Always remember to comment your code!
When writing particularly complex code in
dplyrorggplot2, this includes commenting within a flow of%>%or+operators. See the lecture notes for some examples of this.